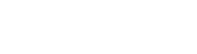NOx Furnace Control Technology
 |
Technical Introduction
|
|
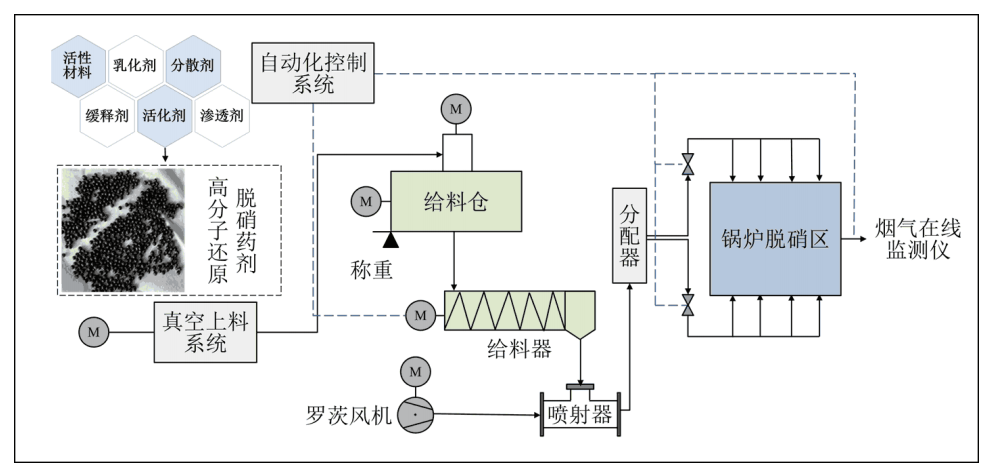
NOx In-furnace Control Technology:
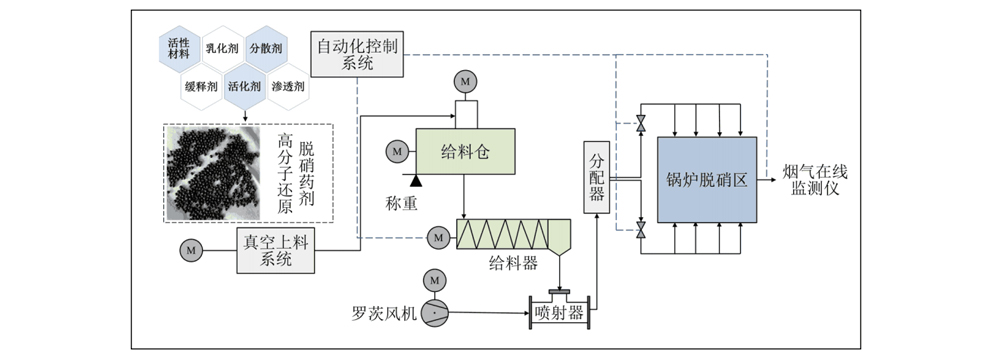
NOx In-furnace Control Technology involves the integrated use of "flue gas recirculation, selective non-catalytic reduction (SNCR), and dry denitrification" techniques. Flue gas recirculation low-Nox combustion technology reduces oxygen content in the localized areas of the incinerator by injecting recirculating flue gas. This action inhibits the formation of fuel-type nitrogen oxides thus minimizing NOx emissions. SNCR denitrification technology involves injecting ammonia or urea solution into the furnace or flue at the specific temperature zones. This process selectively reduces nitrogen oxides in the flue gas to harmless nitrogen gas and water effectively reducing NOx emissions. Dry denitrification technology involves converting nitrogen oxides in flue gas into harmless gases such as nitrogen to improve denitrification efficiency. This method contributes to overall NOx reduction in the flue gas. |
Highlights

Advantages of Flue Gas Recirculation Technology:
|
Broad spectrum approach Compatible with SNCR technology
|
|
Emission Reduction Significantly reduce NOx generation
|
|
Enhanced Flexibility Replacing SCR can save over 10 meters in plant length |
|
Economic Advantage Enhancing plant-wide thermal efficiency and reduce reductant consumption
|
Advantages of Dry Denitrification Technology:
|
Broad spectrum approach Compatible with SNCR technology
|
|
Enhanced Flexibility Replacing SCR can save over 10 meters in plant length
|
|
Economic Advantage Low investment in equipment, by replacing SCR systems in part of the project
|
|
|
Technical Applications

Flue Gas Recirculation:
Operated Projects: Qingdao Xiaojianxi Phase II, Qingdao Huangdao, Gaoling, Zhuhai Phase II, Guangshan, Minhou, Hangzhou Dajiangdong, Huangyan, Nanchang
1. SNCR + EGR process: Achieving NOx stabilization below 100 mg/Nm3, comparable to SNCR +SCR;
2. Enhanced Efficiency: 30% Reduction in ammonia consumption with SNCR + EGR process
3. Improved Thermal Efficiency: Replacement of EGR with SCR results in 4-6% increase in plant thermal efficiency. This process also saves SCR steam and reduces system resistance.
Pollution Control and Resource Utilization (PNCR):
Operated Projects: Gaoling and Guangshan waste-to-energy projects, and Guangshan Biomass Project.
|
Technical Introduction
|
|
NOx In-furnace Control Technology
NOx In-furnace Control Technology involves the integrated use of "flue gas recirculation, selective non-catalytic reduction (SNCR), and dry denitrification" techniques. Flue gas recirculation low-Nox combustion technology reduces oxygen content in the localized areas of the incinerator by injecting recirculating flue gas. This action inhibits the formation of fuel-type nitrogen oxides thus minimizing NOx emissions. SNCR denitrification technology involves injecting ammonia or urea solution into the furnace or flue at the specific temperature zones. This process selectively reduces nitrogen oxides in the flue gas to harmless nitrogen gas and water effectively reducing NOx emissions. Dry denitrification technology involves converting nitrogen oxides in flue gas into harmless gases such as nitrogen to improve denitrification efficiency. This method contributes to overall NOx reduction in the flue gas. |
Highlights

Advantages of Flue Gas Recirculation Technology:
|
Broad spectrum approach Compatible with SNCR technology
|
|
Emission Reduction Significantly reduce NOx generation
|
|
Enhanced Flexibility
Replacing SCR can save over 10 meters in plant length |
|
Economic Advantage Enhancing plant-wide thermal efficiency and reduce reductant consumption
|
Advantages of Dry Denitrification Technology:
|
Broad spectrum approach Compatible with SNCR technology |
|
Enhanced Flexibility Replacing SCR can save over 10 meters in plant length
|
|
Economic Advantage Low investment in equipment, by replacing SCR systems in part of the project
|
|
|
Technical Applications

Flue Gas Recirculation:
Operated Projects: Qingdao Xiaojianxi Phase II, Qingdao Huangdao, Gaoling, Zhuhai Phase II, Guangshan, Minhou, Hangzhou Dajiangdong, Huangyan, Nanchang
1. SNCR + EGR process: Achieving NOx stabilization below 100 mg/Nm3, comparable to SNCR +SCR;
2. Enhanced Efficiency: 30% Reduction in ammonia consumption with SNCR + EGR process
3. Improved Thermal Efficiency: Replacement of EGR with SCR results in 4-6% increase in plant thermal efficiency. This process also saves SCR steam and reduces system resistance.
Pollution Control and Resource Utilization (PNCR):
Operated Projects: Gaoling and Guangshan waste-to-energy projects, and Guangshan Biomass Project.