Deep Waste Heat Recovery and Supply Technology
 |
Technical Introduction
|
|
Deep Waste Heat Recovery and Supply Technology:
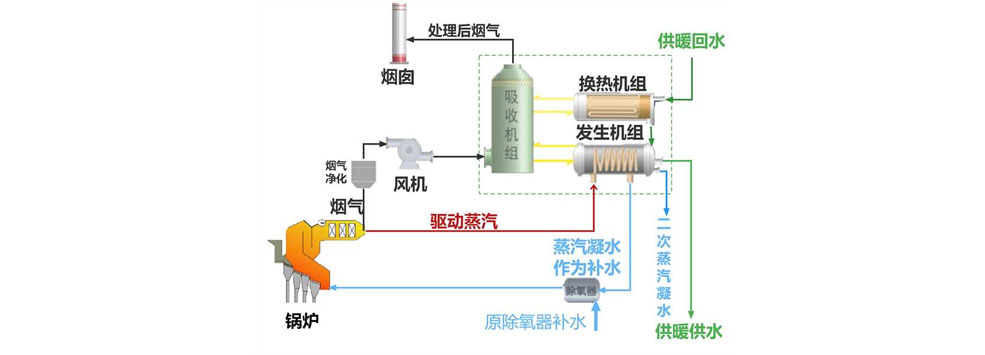
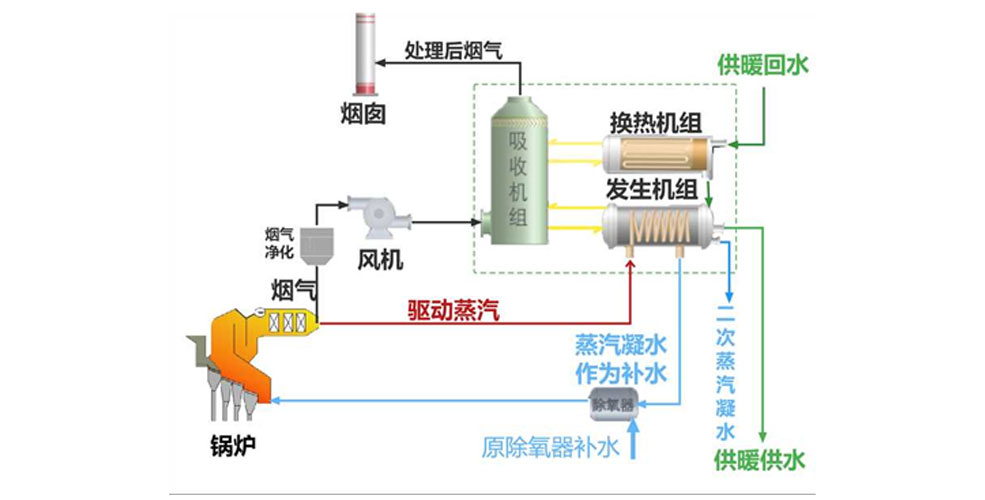
The deep waste heat recovery and supply technology contains four types of waste heat utilization techniques: Deep waste heat utilization of flue gas, deep waste heat utilization of circulating water, deep waste heat utilization of turbine exhaust steam, and tail flue gas waste heat utilization. Flue gas depth waste heat utilization involves recovering heat released from flue gas and water vapor released during combustion. Circulating water depth waste heat utilization refers to the cold effect produced by the evaporator to absorb heat from the heat source at point A. The absorber and condenser produce a thermal effect that heats up the heat source at point B forming an energy cycle. After reheating the heat source at B, the thermal effect is exactly the same as that of the driving heat source needed in production, forming an energy cycle. Deep waste heat utilization of turbine exhaust steam refers to the heating period during which the heat network water is connected to the turbine condenser as circulating water. The spent steam generated by the turbine directly heats the heat network water for heating purposes. Tail flue gas waste heat utilization refers to the use of the constant temperature characteristics of deaerator outlet water and then configuring the temperature control. The waste heat from the waste incineration boiler system tail exhaust (the temperature is usually around 150 ℃, and the SCR system exhaust temperature is set up to 180 ℃ or more) is used to heat the condensation of the water recycling, forming an independent closed loop water system.
|
Highlights

|
Integration of technologies Integration of dehumidification, dust removal, acid removal, and energy recovery
|
|
Achieving High energy efficiency Comprehensive energy utilization of the whole plant leveraging deep utilization of flue gas waste heat or recovery of spent steam heat energy Maximize energy utilizing both power generation and heating/warming applications resulting in efficiency reaching ≥ 60% |
|
Excellent economic efficiency Designed to maximize operating cost savings
|
Technical Applications

Daimyo Tail Gas Deep Waste Heat Utilization Project and Qingdao West Coast Project have the capacity to supply residential heating for an area totaling 1.3 million square (㎡) meters..
|
Technical Introduction
|
|
Deep Waste Heat Recovery and Supply Technology:
The deep waste heat recovery and supply technology contains four types of waste heat utilization techniques: Deep waste heat utilization of flue gas, deep waste heat utilization of circulating water, deep waste heat utilization of turbine exhaust steam, and tail flue gas waste heat utilization. Flue gas depth waste heat utilization involves recovering heat released from flue gas and water vapor released during combustion. Circulating water depth waste heat utilization refers to the cold effect produced by the evaporator to absorb heat from the heat source at point A. The absorber and condenser produce a thermal effect that heats up the heat source at point B forming an energy cycle. After reheating the heat source at B, the thermal effect is exactly the same as that of the driving heat source needed in production, forming an energy cycle. Deep waste heat utilization of turbine exhaust steam refers to the heating period during which the heat network water is connected to the turbine condenser as circulating water. The spent steam generated by the turbine directly heats the heat network water for heating purposes. Tail flue gas waste heat utilization refers to the use of the constant temperature characteristics of deaerator outlet water and then configuring the temperature control. The waste heat from the waste incineration boiler system tail exhaust (the temperature is usually around 150 ℃, and the SCR system exhaust temperature is set up to 180 ℃ or more) is used to heat the condensation of the water recycling, forming an independent closed loop water system.
|
Highlights

|
Integration of technologies Integration of dehumidification, dust removal, acid removal, and energy recovery
|
|
Achieving High energy efficiency
Comprehensive energy utilization of the whole plant leveraging deep utilization of flue gas waste heat or recovery of spent steam heat energy Maximize energy utilizing both power generation and heating/warming applications resulting in efficiency reaching ≥ 60%
|
|
Excellent economic efficiency Designed to maximiz operating cost savings |
Technical Applications

Daimyo Tail Gas Deep Waste Heat Utilization Project and Qingdao West Coast Project have the capacity to supply residential heating for an area totaling 1.3 million square (㎡) meters.