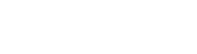Low Carbon Eco-Industrial Park Synergy Technology
 |
Technical Introduction
|
|
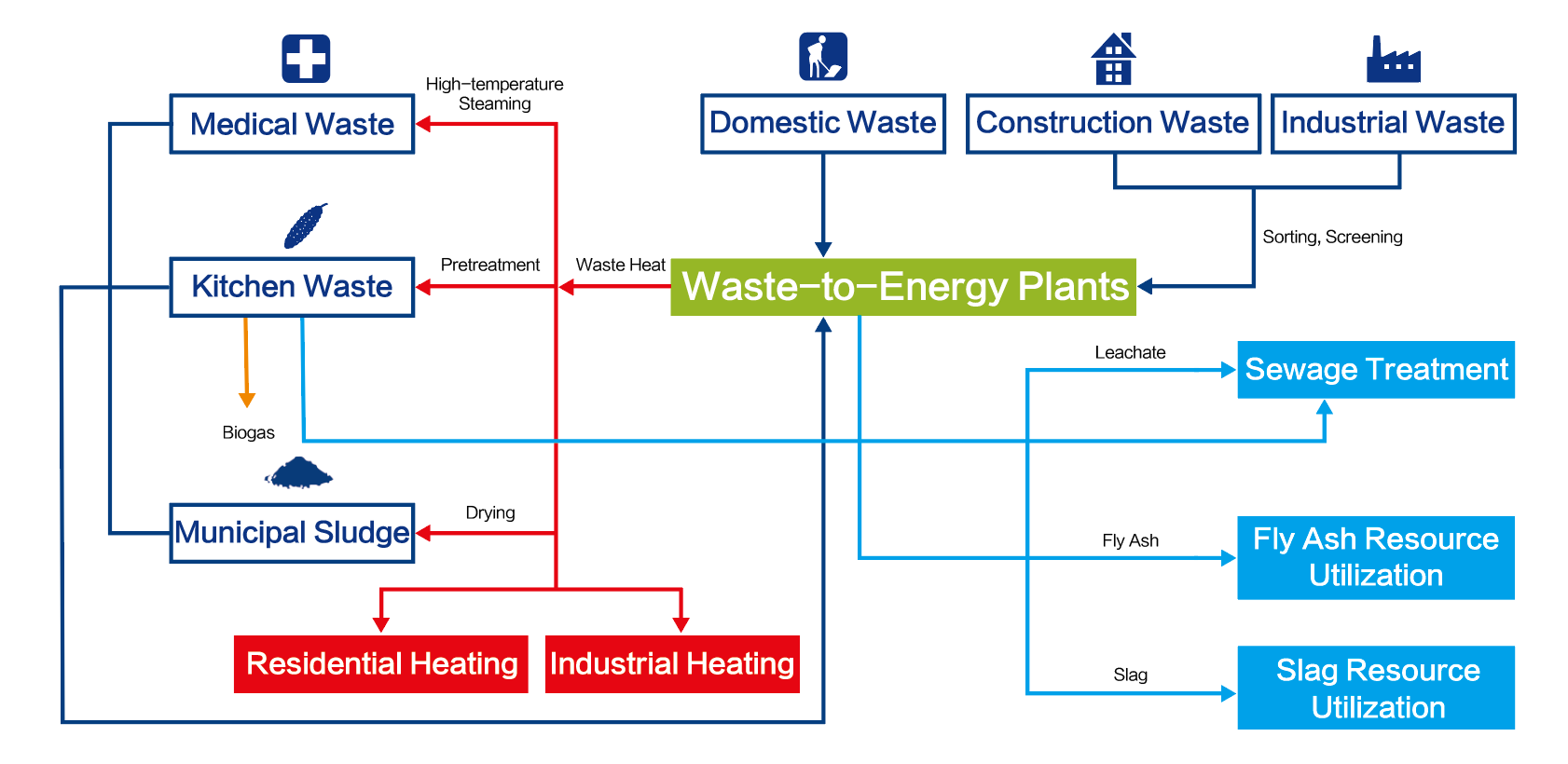
Low Carbon Eco-Industrial Park Synergy Technology: The initiative is focused on waste-to-energy solutions, integrating various waste streams including municipal sludge, medical waste, food waste, and construction waste into a comprehensive treatment approach. In the Low Carbon Eco-Industrial Park, waste heat generated from waste-to-energy processes can be utilized for activities such as sludge drying, kitchen fermentation, and high temperature treatment of medical waste. Additionally, combustible residues from various solid waste treatment can be recycled back into the incinerator for energy generation, enabling the efficient recycling of materials and energy sources. |
Highlights

|
High resource utilization Maximized recycling of materials and energy
|
|
Management Efficiency Maximize operational efficiency with park collaboration
|
|
Low Environmental Impact Low carbon production with ultra-low emissions
|
|
Low Investment Cost Multiple uses in one park to optimize economic benefits |
|
Low operating costs Recycling of renewable energy sources reduces economic costs |
|
Industrial parks cover a small area Sharing park facilities with the public, turning NIMBY (Not In My back Yard) to PIMBY (Please in My Back Yard) |
Technology Application

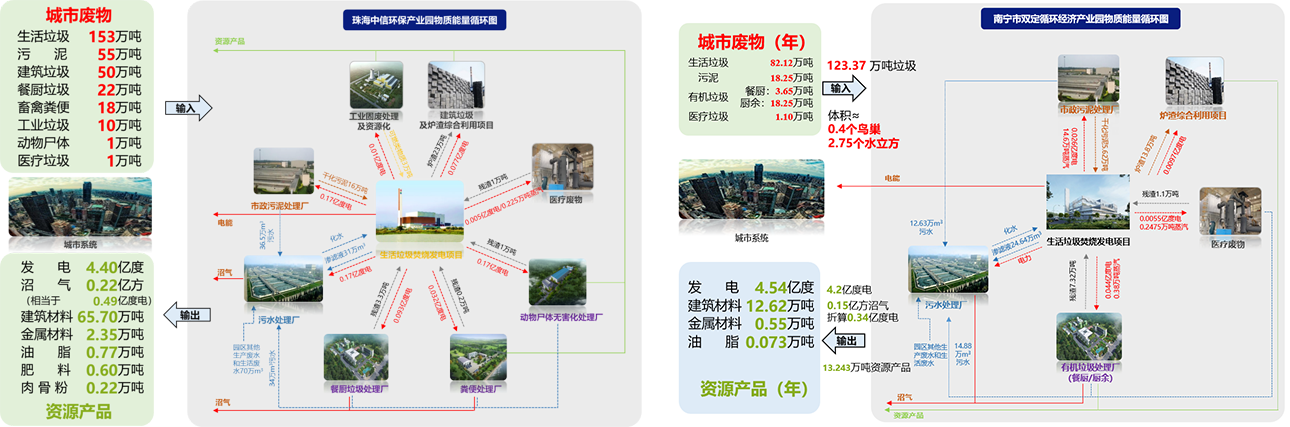
As of December 2022, SUS has made significant investments in and successfully operated a total of 15 low-carbon eco-industrial parks. Among these, two waste-to-energy plants stand out for their remarkable contribution to emission reduction. The waste-to-energy plant in Zhuhai CITIC Environmental Protection Industrial Park has been instrumental in reducing emissions by approximately 40,000 tons annually by efficiently converting waste into energy and supplying power and heat to other facilities in the park.
The waste-to-energy plant in the Shuangding Circular Economy Industrial Park in Nanning City has demonstrated even greater emission reduction capabilities amounting to approximately 65,000 tons annually by supplying electricity and heat to various facilities within the park.
|
Technical Introduction
|
|
Low Carbon Eco-Industrial Park Synergy Technology: The initiative is focused on waste-to-energy solutions, integrating various waste streams including municipal sludge, medical waste, food waste, and construction waste into a comprehensive treatment approach. In the Low Carbon Eco-Industrial Park, waste heat generated from waste-to-energy processes can be utilized for activities such as sludge drying, kitchen fermentation, and high temperature treatment of medical waste. Additionally, combustible residues from various solid waste treatment can be recycled back into the incinerator for energy generation, enabling the efficient recycling of materials and energy sources. |
Highlights:

|
High resource utilization Maximized recycling of materials and energy
|
|
Management Efficiency Maximize operational efficiency with park collaboration
|
|
Low Environmental Impact Low carbon production with ultra-low emissions
|
|
Low Investment Cost Multiple uses in one park to optimize economic benefits
|
|
Low operating costs Recycling of renewable energy sources reduces economic costs
|
|
Industrial parks cover a small area Sharing park facilities with the public, turning NIMBY (Not In My back Yard) to PIMBY (Please in My Back Yard)
|
Technology Application

As of December 2022, SUS has made significant investments in and successfully operated a total of 15 low-carbon eco-industrial parks. Among these, two waste-to-energy plants stand out for their remarkable contribution to emission reduction. The waste-to-energy plant in Zhuhai CITIC Environmental Protection Industrial Park has been instrumental in reducing emissions by approximately 40,000 tons annually by efficiently converting waste into energy and supplying power and heat to other facilities in the park.
The waste-to-energy plant in the Shuangding Circular Economy Industrial Park in Nanning City has demonstrated even greater emission reduction capabilities amounting to approximately 65,000 tons annually by supplying electricity and heat to various facilities within the park.

- Prev:None
- Next:None